Neurological diseases(e.g., Myasthenia gravis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, Multiple sclerosis)

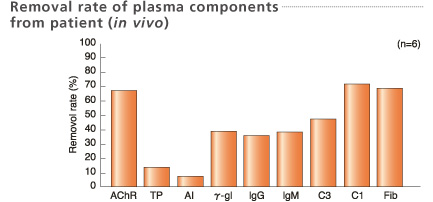
Plasma samples were collected at the inlet and outlet of the column when 1L plasma was treated.
*AChR: Acetylcholine receptor
Shibuya et al. [Article in Japanese] Chiryo 66 : 49-55, 1984
Blood samples for removal rate were collected before and after treatment.
Treated plasma volume: 2L
Shibuya et al. Current Practice in Therapeutic Plasmapheresis 166-172, 1985
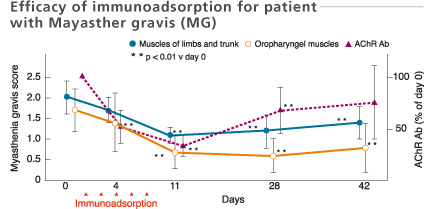
Mean values of myasthenia gravis score and titer of AChR antibodies in the 11 improved patients after immunoadsorption therapy. Consecutive immunoadsorption treatments induced a significant fall of the myasthenia gravis score and a decrease in the titer of AChR antibodies. The myasthenia gravis score remained low even on day 42 despite the rise in AChR antibody titers.
Shibuya et al. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57: 578-581, 1994
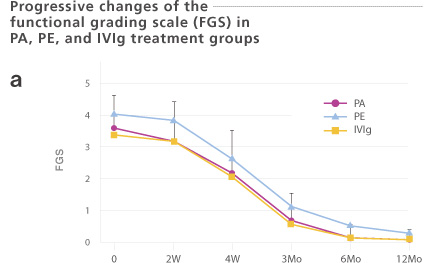
Sixty-three Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) patients were enrolled. These patients were treated with plasma adsorption (PA, n=39: Immusorba TR-350), plasma exchange (PE, n=14), or immunoglobulin treatment (IVIg, n=10). The number of days required for one or two functional grades improvement was 20.3 ±15.3 or 34.8 ± 20.5 days, respectively. Treatment methods (PA, PE, or IVIg) did not significantly influence the outcome. Since PA does not result in a risk of unknown infection, choosing a PA may be justified.
Seta et al. Factors influencing outcome in Guillain-Barré Syndrome: comparison of plasma adsorption against other treatments. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 107(6): 491-496, 2005
| Adsorbent | Material | Tryptophan immobilized polyvinylalcohol gel |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | 350 mL | |
| Priming Volume | 300 mL | |
| Container | Material | Polypropylene |
| Dimension | 211mm[L] x 62mm[D] | |
| Weight | 650g | |
| Sterilization | High pressure steam | |
| Filter | Material | Polyethylene (coated with ethylene-vinylalcohol copolymer) |
|---|---|---|
| Area | 0.07 m2 | |
| Container | Material | Poly (vinyl chloride) |
| Dimension | 165mm[L] x 22mm[D] | |
| Priming Volume | 30 mL | |
| Sterilization | Ethylene oxide | |
For patients undergoing treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, there is a possibility that treatment with the IMMUSORBA TR-350 will lead to a drop in blood pressure. Simultaneous treatment with ACE inhibitor and the IMMUSORBA TR-350 must be avoided.
The IMMUSORBA TR-350 is intended for the treatment of plasma. Never run whole blood through the IMMUSORBA TR-350. Thrombocytes cannot pass through the IMMUSORBA TR-350 and may cause blockage.
Do not use IMMUSORBA TR-350 with plasma containing a large amount of thrombocytes.